本文列举了简单的数值方法:Euler 方法、后退 Euler 方法、梯形公式、改进 Euler 方法,并用 MATLAB 求解线性 ODE,最后展示了输出结果。
常微分方程初值问题
考虑常微分方程初值问题,设
$$\left\lbrace\begin{aligned} &\frac{d u}{d t}=f(t, u), \quad 0<t \leqslant T \\ & u(0)=0\end{aligned}\right.$$
$f(t, u)$ .在区域$ \mathrm{G}: 0 \leqslant t \leqslant T,|u|<\infty $上连续,求$u = u (t)$:满足:
$$\left \lbrace \begin{aligned}&\frac{d u}{d t}=f(t, u), \quad 0<t \leqslant T \ &u(0)=0\end{aligned}\right.$$
通常 $f $ 满足 Lipschitz 条件:$\left|f\left(t, u_{1}\right)-f\left(t, u_{2}\right)\right| \leqslant L\left|u_{1}-u_{2}\right|$
线性 ODE 例子
$$\left{\begin{aligned}&\frac{d u}{d t}=t^{2}+t-u, \quad t \in [0,1] \ &u(0)=0\end{aligned}\right.$$
方程的真解:$u(x)=-e^{-t}+t^{2}-t+1$
Euler 方法
$$u_{n+1}=u_{n}+h f\left(t_{n}, u_{n}\right)$$
Euler 方法数值求解
MATLAB 程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| % Euler1.m
% Euler method for the ODE model
% u'(x)=x^2+x-u, x in [0,1]
% Initial condition: u(0)=0 ;
% Exact solution: u(x)=-exp(-x)+x^2-x+1.
clear all; clf
h=0.1;
x=0:h:1; % function interval
N=length(x)-1;
u(1)=0; % initial value
fun=@(t,u) t.^2+t-u; % RHS
for n=1:N
u(n+1)=u(n)+h.*fun(x(n),u(n));
end
ue=-exp(-x)+x.^2-x+1; % exact solution
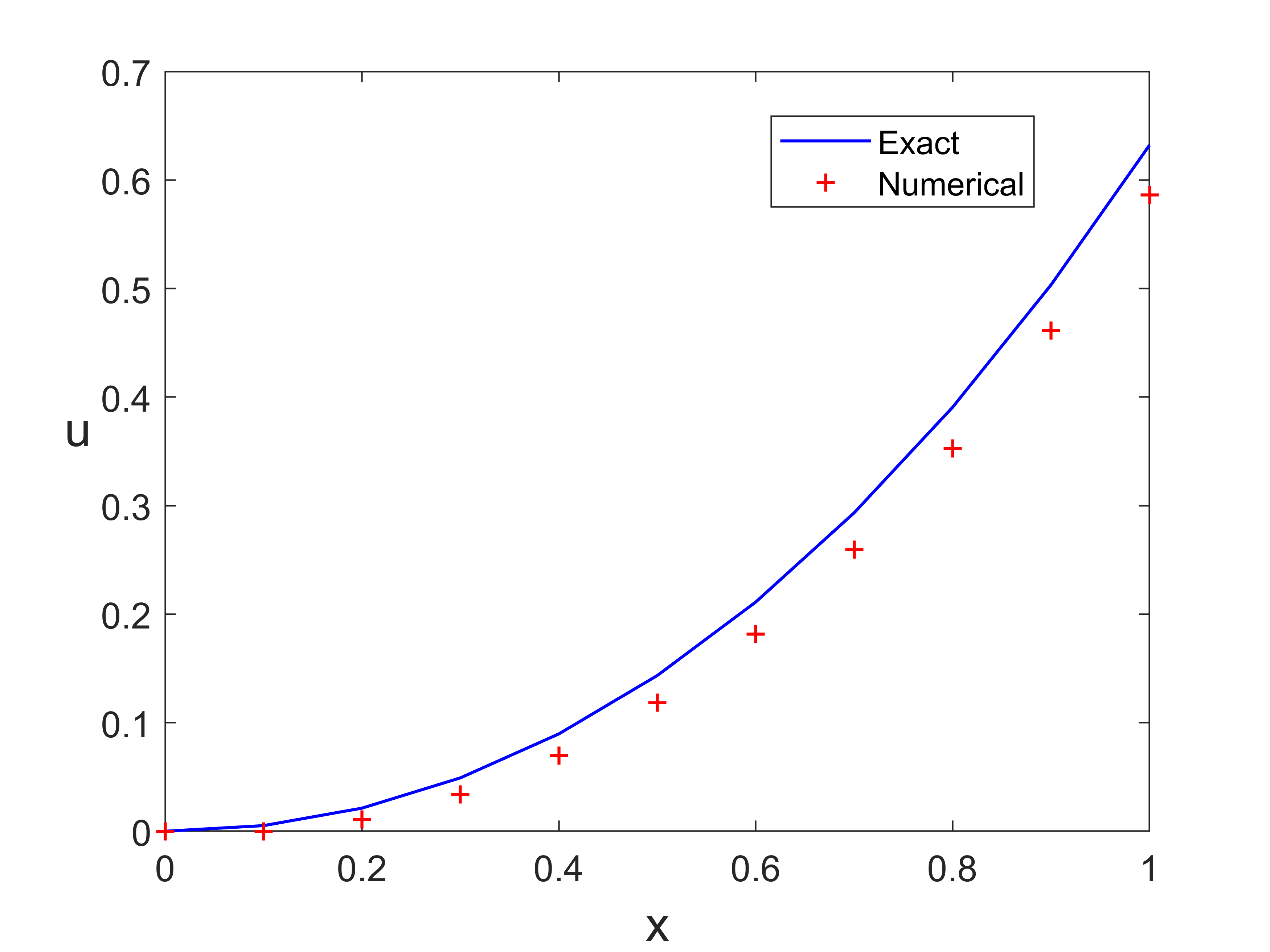
plot(x,ue,'b-',x,u,'r+','LineWidth',1)
legend('Exact ','Numerical','location','North')
set(gca,'fontsize',12)
xlabel('x','fontsize', 16), ylabel('u','fontsize',16,'Rotation',0)
% print -dpng -r600 Euler1.png
|
输出结果
![Euler1.png]()
后退 Euler 方法
$$u_{n+1}=u_{n}+h f\left(t_{n+1}, u_{n+1}\right)$$.
梯形公式
$$u_{n+1}=u_{n}+\frac{h}{2}\left[f\left(t_{n}, u_{n}\right)+f\left(t_{n+1}, u_{n+1}\right)\right]$$.
梯形公式数值求解
梯形公式与后退 Euler 方法类似,这里考虑梯形公式,对于线性 ODE 例子:
$$u_{n+1}=u_{n}+\frac{h}{2}\left[t_{n}^{2}+t_{n}-u_{n}+t_{n+1}^{2}+t_{n+1}-u_{n+1}\right]$$
可得
$$u_{n+1}=\frac{2-h}{2+h} u_{n}+\frac{h}{2+h}\left[t_{n}^{2}+t_{n}+t_{n+1}^{2}+t_{n+1}\right]$$
MATLAB 程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| % Trapezoidal.m
% Trapezoidal rule for the ODE model
% u'(x)=x^2+x-u, x in [0,1]
% Initial condition: u(0)=0 ;
% Exact solution: u(x)=-exp(-x)+x^2-x+1.
clear all; clf
h=0.1;
x=0:h:1; % function interval
N=length(x)-1;
u(1)=0; % initial value
for n=1:N
u(n+1)=(2-h)/(2+h).*u(n)+h/(2+h).*(x(n)^2+x(n)+x(n+1)^2+x(n+1));
end
ue=-exp(-x)+x.^2-x+1; % exact solution
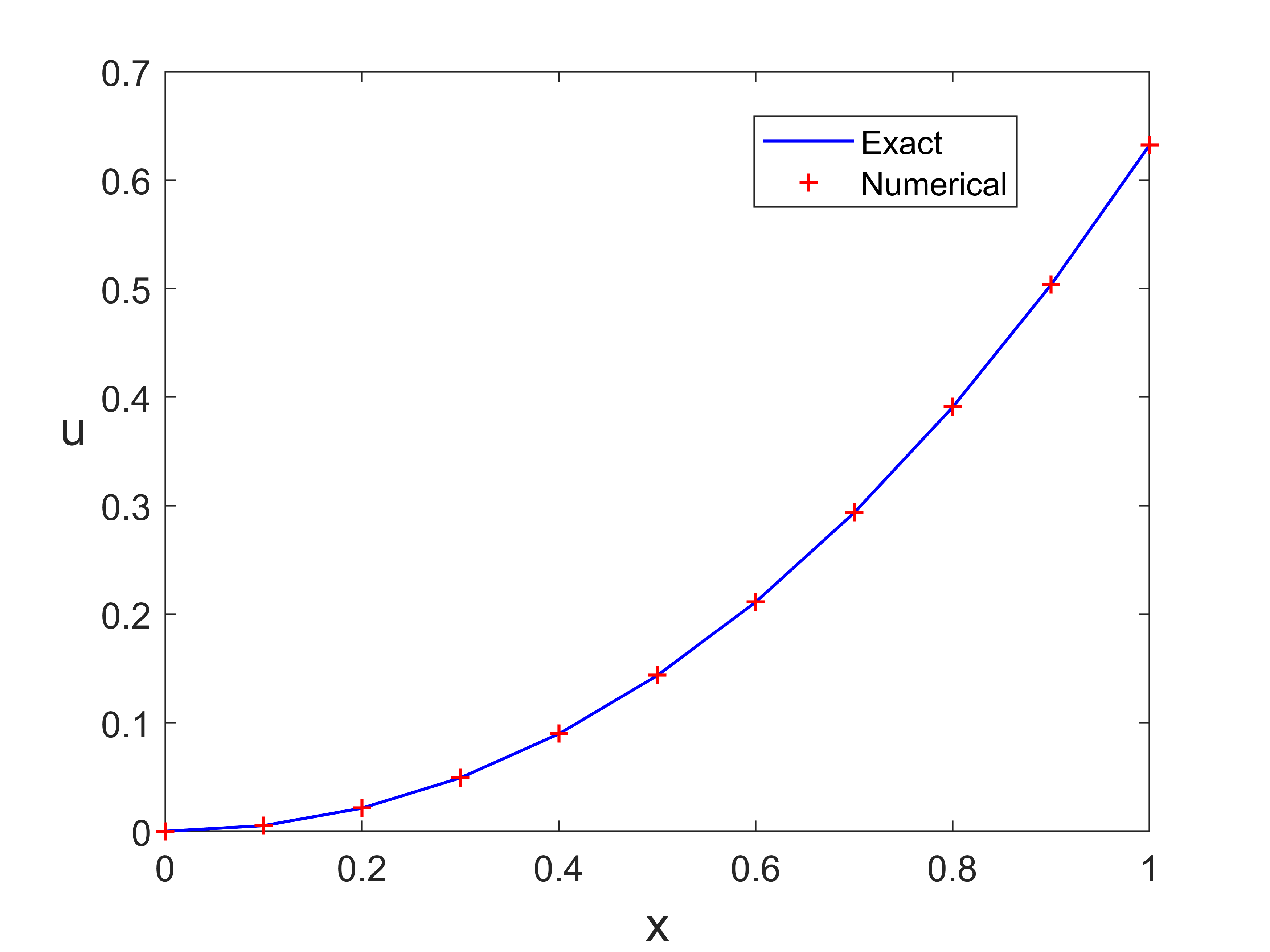
plot(x,ue,'b-',x,u,'r+','LineWidth',1)
legend('Exact ','Numerical','location','North')
set(gca,'fontsize',12)
xlabel('x','fontsize', 16), ylabel('u','fontsize',16,'Rotation',0)
% print -dpng -r600 Trapezoidal.png
|
输出结果
![Trapezoidal.png]()
改进的 Euler 方法
预估校正
$$\left \lbrace
\begin{aligned}&\bar{y}_{n+1}=y_{n}+hf(x_{n},y_{n}) \\
&y_{n+1}=y_{n}+\frac{h}{2}[f(x_{n},y_{n})+f(x_{n+1},\bar{y}_{n+1})]
\end{aligned}
\right.$$
MATLAB 程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| % EulerPro.m
% Modified Euler method for the ODE model
% u'(x)=x^2+x-u, x in [0,1]
% Initial condition: u(0)=0 ;
% Exact solution: u(x)=-exp(-x)+x^2-x+1.
clear all; clf
h=0.1;
x=0:h:1; % function interval
N=length(x)-1;
u(1)=0; % initial value
fun=@(x,u) x.^2+x-u; % RHS
for n=1:N
k1=fun(x(n),u(n));
k2=fun(x(n+1),u(n)+h*k1);
u(n+1)=u(n)+(h/2)*(k1+k2);
end
ue=-exp(-x)+x.^2-x+1; % exact solution
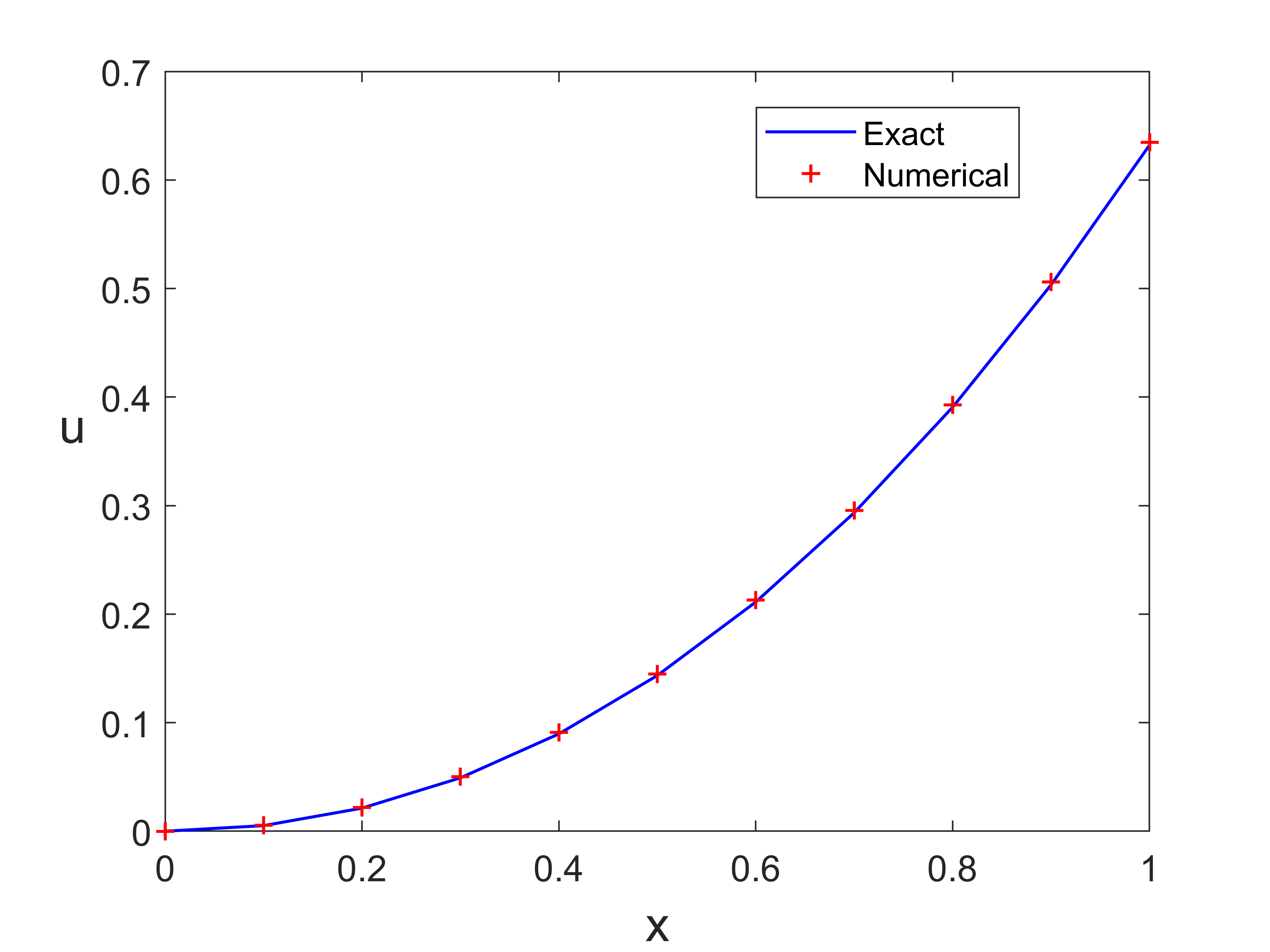
plot(x,ue,'b-',x,u,'r+','LineWidth',1)
legend('Exact','Numerical','location','North')
set(gca,'fontsize',12)
xlabel('x','fontsize', 16), ylabel('u','fontsize',16,'Rotation',0)
% print -dpng -r600 EulerPro.png
|
输出结果
![EulerPro.png]()
参考书籍
数值分析 第 5 版 (李庆扬等)
MATLAB 微分方程高效解法
微分方程数值解法(第四版)李荣华